 |
| March 13, 2018 | Volume 14 Issue 10 |
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
Wheels:
First crankshaft integrated starter-generator system for 48-V hybrid vehicles
The demand for 48-V hybrid vehicles, which offer excellent fuel efficiency at relatively affordable costs, is expected to increase, especially in Europe.
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation has begun mass-producing the auto industry's first crankshaft-mounted integrated starter-generator (ISG) system for 48-V hybrid vehicles, which will be mounted in future Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
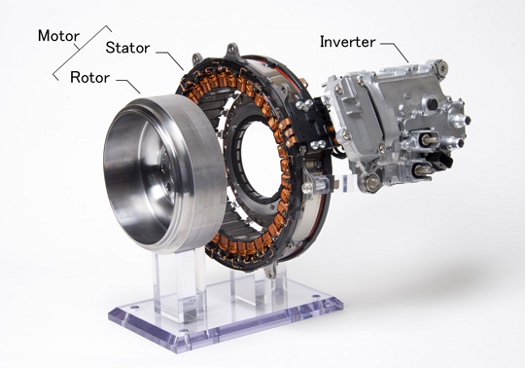
Mitsubishi crankshaft ISG system for 48-V hybrid.
Mitsubishi Electric developed its ISG system -- a crankshaft direct-driven system for idling-stop-start, energy recovery, and torque assist -- to achieve higher output power and better fuel efficiency in 48-V hybrid vehicles. Mitsubishi Electric says it will continue developing increasingly smaller, lighter-weight, and higher-power ISG systems to increase fuel efficiency and reduce CO2 emissions.
System features
- Crankshaft-mounted motor realizes excellent fuel efficiency.
- Compared to belt-driven starter-generators, the crankshaft-mounted motor produces higher output power and generates more power, which contributes to better fuel efficiency.
- Thin-profile, high-power motor for more flexible installations.
- Mitsubishi Electric's original coil winding technology realizes a high-density configuration for thick coils required in a 48-V high-current motor.
- Thin-profile, higher-power motors adapt flexibly to various vehicle layouts.
- Compact, highly reliable inverter.
- Newly developed transfer-molded power module for 48-V systems reduces heat resistance and enhances durability.
- Optimally designed cooling unit enhances cooling performance to realize a compact, highly reliable inverter.
Belt-driven and engine crankshaft direct-driven systems
- Belt-driven system: Using a belt to transfer power from the motor to the engine can limit both maximum torque with abrupt force transmission and the motor's peak power output.
- Engine crankshaft direct-driven system: Connecting the motor directly to the engine crankshaft eliminates the limitations of the belt system and enhances both motor output power and power generation
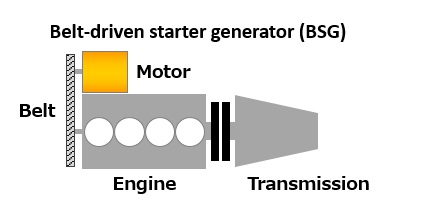
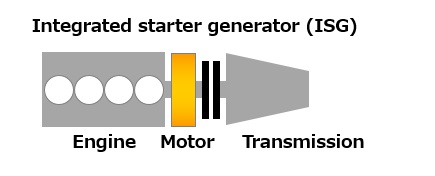
Source: Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
Published March 2018
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy
